Introduction
“Though the problems of the world are increasingly complex, the solutions remain embarrassingly simple.”
-Bill Mollison
Permaculture is the study and practice of sustainable living. At its core, Permaculture is a method of living in harmony with the world around us, and creating abundance from it. Long before Bill Mollison and David Holmgren, the naturalist and academic considered the co-founders of permaculture, coined the term in the 1970s, people were living in communities guided by its principles, and adapting to a changing world as their ancestors had done for generations.
This handbook is a concise overview of the basic techniques, principles and values that are frequently taught in a Permaculture Design Course (PDC), a 72-hour class that provides an overview of the principles and projects behind holistic community. Thousands of people have taken part in such courses all over the world, several dozens in classes I facilitated in communities in Thailand, Laos, Nepal and India.
If you want to live more closely in tune with nature, to live a simpler life and to meet other folks who want the same, this book is an introduction. You will learn what permaculture is and how you can apply it to your life, in a short amount of time.
This course aims to provide an overview of permaculture’s principles, lay out some core permaculture techniques and practices, and provide direction and resources for connecting with people who share a passion for this work.
Permaculture Principles
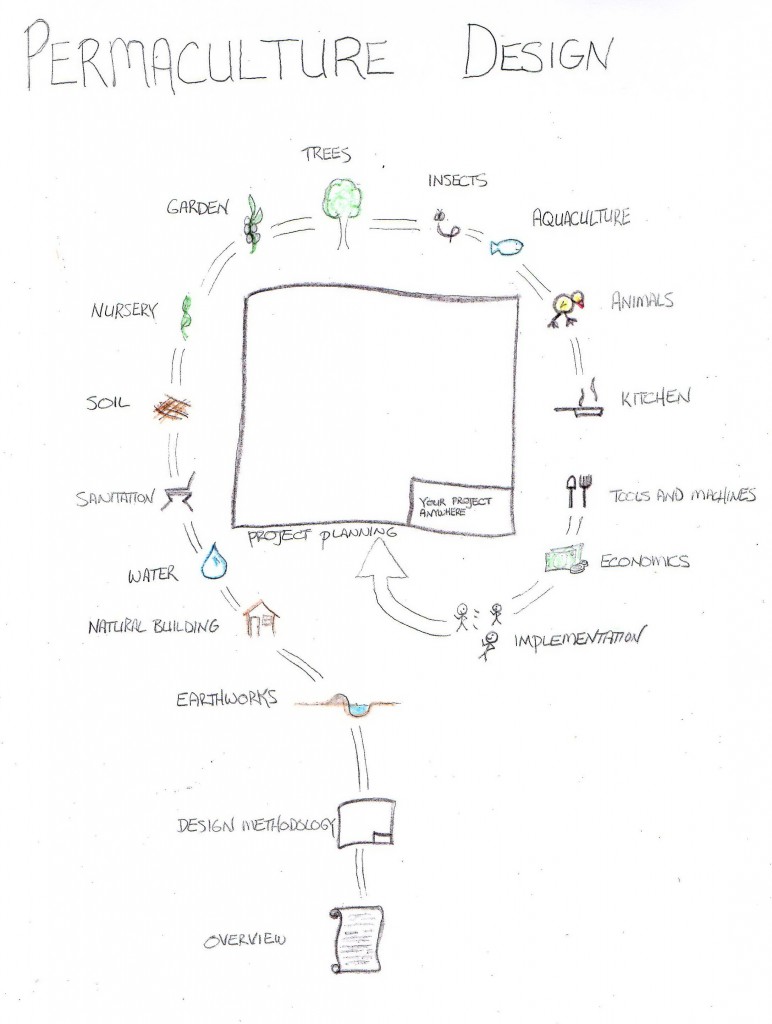
The overall goal of permaculture is to be self-reliant by producing a surplus of food water and energy within a site. Here is a list of more specific goals as they relate to each chapter:
- Earthworks – Capture rainwater and provide access to the site
- Natural building – Provide housing for people and animals
- Water – Clean, conserve and reuse water
- Sanitation – Produce no waste
- Soil – Build healthy soil
- Nursery – Propagate plants
- Garden – Grow and harvest edible plants
- Trees – Grow useful trees and food forests
- Aquaculture – Raise healthy fish and plants
- Insects – Raise beneficial insects and keep pests away
- Animals – Raise healthy animals using the resources available
- Kitchen – Prepare, ferment or preserve food grown on site
- Tools and technology – Use energy efficiently
- Economics – Create a surplus
- Project planning – Install a permaculture design
Permaculture Ethics
- People care – Be considerate of everyone’s time, interests thoughts and actions, including your own.
- Earth care – Care for the earth, animals, plants, trees, fungi, micro-organisms, water and air and everything else.
- Fair share – Fairly distribute surplus, if there is any.