
Principle: Raise healthy fish and plants
Aquaculture is the name of any type of water or wetlands where water animals and plants are grown in support of each other. Ponds, chinampas, or indoor or smaller units are common permaculture elements. Aquaculture can produce more protein and produce per area of land than any other growing system.
Aquaculture systems can be implemented on all types of land: on swamps, wetlands, ponds or on land, on terraces and swales. It assists with drainage and water flow during the wet season and can be used as water storage for the dry season. This system can also be combined with other animals such as ducks, chickens, pigs to increase productivity of all systems.
Aquaculture in ponds
Aquaculture in a pond works great. Fish as well as the water, oxygen, sunlight, pond shape, plants, trees and other animals all play an important role in pond aquaculture systems. Here are some design considerations when installing your pond:
- Oxygen – Oxygenated water is essential for a healthy pond. To add oxygen to water, you can add water plants or a submersible pump.
- Location – The pond should be near a place with a continual supply of fresh water such as a water tap or rainwater collection tank or be the drainage spot for nearby earthworks.
- Sunlight – Plant trees and plants around the pond edge to shade the pond. This reduces water evaporation and provides a cooler temperature for the fish. Also, adding banana trees to the pond provides partial shade and a place for algae to grow.
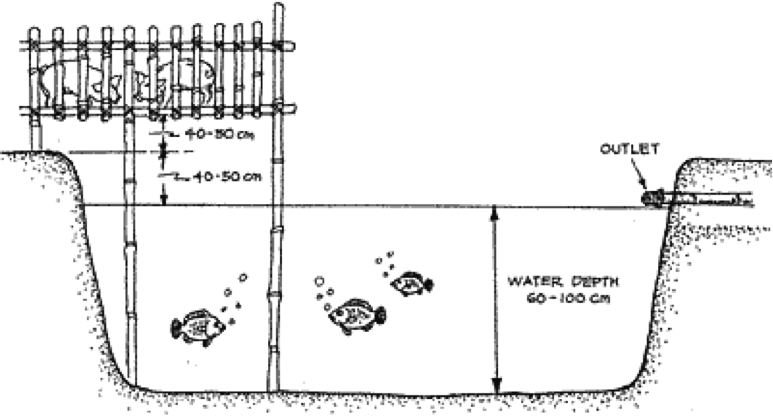
- Size – It’s better to make many smaller ponds rather than one large pond. To keep the water cool, the pond size should be a minimum of 3m x 3m, 5m x 5m – 10m x 10m is a good manageable size. Add a drainage pipe during the construction of the pond to direct overflow into another pond or swale system.
- Depth – A variety of depths in a pond provides a cool place for fish to avoid hot sun and hide from predators. A shelf around the edge and deeper section in the middle is one way to shape your pond. Shallow depths should be 30-50cm deep and deep areas should be at least 1-2m deep.
- Shape – A fishpond can be made any shape you like, but more edge is best. More edge = more veg = more fish food = more fish.
- Liner – Clay is easier, cheaper and more eco-friendly, however you need a high clay content to hold water. Animals can also be used to help seal a pond such as pigs. Plastic liner is a good secondary option. Ferro-cement can also be used to reinforce the cement. See earthworks for more pond lining techniques.
Plants
On the pond
Plant areas around the pond edge immediately to hold the soil in place and prevent erosion. Pond edges are very fertile because they receive lots of water and nutrients (Many of the following species were found at: http://plants.ifas.ufl.edu/node/607)
- Floating plants – Water hyacinth, frog’s bit, water fern, bog-mat, banana lily, spatterdock, duckweed, water lettuce, Indian water chestnut, cattail, water spinach, arrow root
- Anchored plants – Morning glory, watercress, water chestnut, willow
- Emergent – Lotus, taro, wild rice, rice, bulrush, reeds, water chestnut, water spinach, cabomba, anacharia, hornwort, arrowhead, blue flag, baby’s tears, cattails, buttonbush, elderberry, golden canna, knotweeds
On the edge of the pond
- Grasses like vetiver, citronella, lemongrass, napier give structure to the soil
- Sweet potato, cassava, tomato, lettuce also grow well
- 1-2m from pond edge – Small fruit trees – Banana, citrus, papaya
- 2-3m from pond edge – Large fruit trees – Mulberry, guava, as well as other legumes
Fish
Many types of fish can be grown using aquaculture. Stocking 3 -5 fish per 1m2 is good for most fishponds. There are three categories of fish:
- Carnivore – eel and catfish (some catfish are omnivore)
- Omnivore – tilapia, gourami, catfish and mujair
- Herbivore – carp
Introduce fish to your pond in the following order:First add herbivore fish, about 3 months later add omnivore fish, about 3 months later, add carnivore fish.
Fish food recipes
- Fish Food Recipe – Grow a grain, harvest it, process it, grind it and mix it with a high-pectin fruit (mango, banana, crabapple). Then put it through a meat grinder extruder to make a uniform shaped strand. Lay this on cookie sheets and dry in the sun until the outside is crunchy and inside is moist. Cut into small bits according to fish size.
- Maggot Bucket Recipe – Drill 1/2cm holes in 5-30 gallon bucket. Then fill the gallon bucket with food and meat scraps. Make sure the contents are plenty moist. Leave it for a few days. Flies will lay eggs, hatch and begin to grow larvae. Feed them to fish or chickens before they hatch.
- Fish Emulsion Recipe – Using a fifty-five gallon bucket or smaller with a tight fighting lid add dead fish and cover them with water until the container is full. Stir occasionally. Cover and seal for 9 months. It will transform into a golden and sweet thick paste and is an amazing source of nutrients and nitrogen.
- Additional fish food ideas
- Fish also like cooked roots such as cassava, taro, sweet potato
- Feed insects, mice, termites and frogs to carnivore fish
- Legume leaves and seeds contain lots of protein and minerals
- Fish also eat moringa seeds and leaves as well as peanuts
Integrating fish with other animal systems
Many types of animal houses can be built on top of a pond so their feces falls straight into the water for fish food. You can build the pen above the water but it’s also good to place the house above the water inlet before entering the pond so that the amount of water entering the pond can be regulated. Here are some general estimations:
Combining fish with other animals
Pond size versus number of chickens:
- A pond of 25m2 (5×5) = 5 chickens, 1-3 pigs or goats
- A pond of 100m2 (10×10) = 5-10 chickens, 3-5 pigs or goats
Chinampas
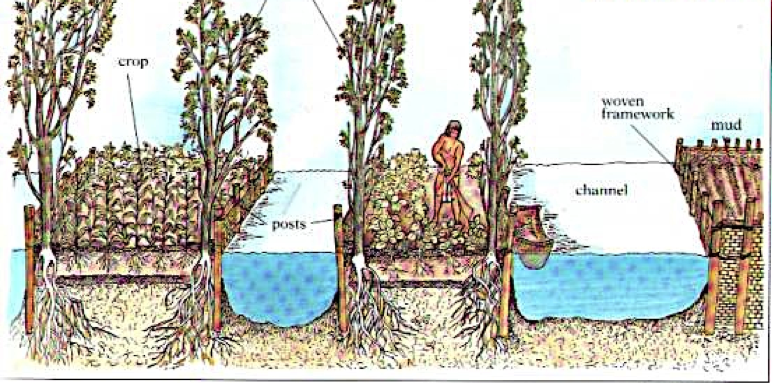
Chinampas are polyculture systems built on raised beds surrounded by canals or swamplands. Chinampas can produce yields 2-3 times greater than flat land farming. Chinampas regulate the microclimate by retaining moisture through capillary action. Annual and perennial crops as well as cover crops and fruit trees grow well on chinampas. Potential yields of chinampas systems:
- 8-14 ton per hectare of potato (versus 1-4 t/ha on flat land)
- 5-6.0 ton per hectare of corn (versus 2.6-4.0 t/ha on flat land)
- 1 hectare can support 15-20 people per hectare per year using chinampa farming
Chinampa systems have been practiced on saline lakes around Mexico, also Peru and Bolivia, for thousands of years. The Aztec people improved the practice by using chinampas for seed germination and seedling nurseries on the sides of the beds. Chinampas were managed by rituals linked to seasons in the solar calendar and to Aztec deities for water and fertility. Farming via chinampas has dramatically declined in recent years as people have switched over to monoculture farming.
Sizing chinampa beds
Chinampa beds can be any size but are commonly 2-4 m wide and 20-40 m long. The raised beds are 0.5-0.7 m above water level, with sides reinforced by branches, willow trees or bamboo, with a thick layer of topsoil on the beds. Soil nutrients are provided from fertile organic wastes from the canal and reservoir bottom.
Aquaponics
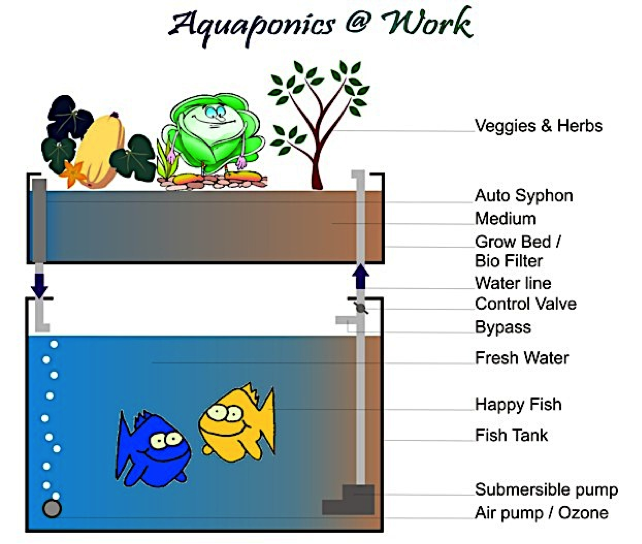
Aquaponics is the cultivation of fish and plants together in a constructed, recirculating ecosystem utilizing natural bacterial cycles to convert fish waste to plant nutrients. Aquaponics harnesses the best attributes of aquaculture and hydroponics without the need for chemical fertilizers or added nutrients – Aquaponics Gardening Community
How do aquaponics work?
- Fish produce waste in the water
- Water is pumped into a trough filled with plants
- Plants filter water that returns to the fish
Food conversion ratio
This is a ratio of the amount of food animals must consume in relation to their physical growth. These statistics support the idea that fish are one of the easiest animals to raise:
Animal lb food : lbs growth
Fish 1½:1
Poultry 2:1
Pigs 4:1
Cattle 7:1
Sheep 8:1
Lighting
For indoor growing, here are some guidelines for proper light intensity: A 1500w H.I.D. (high-intensity discharge) lamp will cover 8’ x 8’ area – 1000w covers 6’ x 6’, 600w covers 5’ x 5’, 400w covers 4’ x 4’, 300w covers 3’ x 3’, 100w covers 1’ x 1’.
System design

- Basic flood and drain – Simplest design, appropriate for 1:1 grow bed to fish tank volume.
- CHOP (Constant Height, One Pump) – Enables 2:1 – 3:1 grow bed to fish tank ratio. More grow beds filtering the water is generally better for the health of the fish
- CHOP2 – Same as CHOP but uses barrels
- NFT – Look online for Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) or Raft technique
Sizing your system
Recommended ratio of grow bed to fish tank is 1:1 to start, move to 2:1 once you get it working.
Media and media depths
Use gravel without limestone or rinse gravel once you acquire it. To rinse limestone off gravel, fill sandbags with gravel and dunk them in a stream. To find out if gravel has limestone in it: Put gravel in a cup of vinegar. If it fizzes, it has limestone. Lime will change the pH of the water. You can also buy expanded clay from a store.
Grow beds should be at least 30cm deep. This encourages bacteria to grow and supports enough density to support plants. Leave the top 5cm dry, the next 20cm for plant roots and the last 5cm for water collection. Fish tanks should be at least 45cm deep.
20L of water can hold 200 fish (at maturity weighs ½ kilo) and water 30cm2 of grow bed.
Fish tank
A round shaped tank is preferable to a square shaped tank. A short and wide shaped tank is better than deep and narrow. Avoid placing the tank in direct sunlight, cover or use shade to keep cool. Warmer water holds less oxygen.
55-gallon oil drum, IBC liquid totes, aquariums, bathtubs or pond liner to make good fish tanks. Go to www.gardenpool.org for other fish tank ideas.
Plumbing system
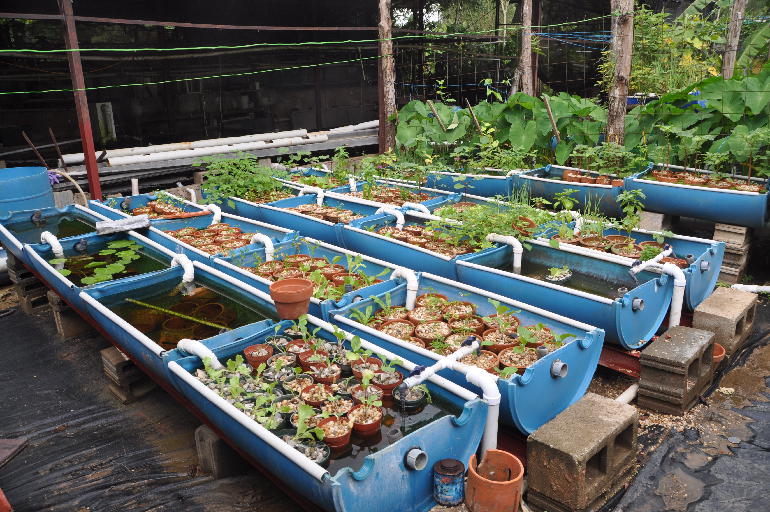

The pump flow rate (measured by liters per hour) should be four times the number of liters in your tank if you fill and drain grow bed 15 minutes every hour (recommended)
Use ½” PVC pipe throughout your aquaponics system. Do not glue the pipes in case you need to change them. You can also assemble an aeration pipe, spray bar or irrigation bar (look online for design) for simple irrigation techniques.
Vertical aquaponics gardening
When growing your aquaponics garden, consider these unique vertical gardening styles: window gardens, PVC towers, zip grow towers, stacking towers (look up online)
Stocking with fish – Choose fish that match the climate where you live. See Pond aquaculture for more information on fish.
Water – If using public water supply, fill up your tank, turn on your pump and run the water through your system for a day or two to remove the chlorine. Or filter it before adding fish.