Principles
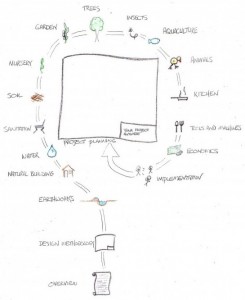
The following are general principles for sustainable farming:
Earthworks – Capture rainwater in the soil and provide access to the site
Natural building – Provide housing for people and animals
Water – Catch, clean, conserve and reuse water
Sanitation – Produce no waste
Soil – Build soil
Microorganisms – Grow microorganisms
Nursery – Save seeds and propagate plants
Plants – Grow and harvest edible plants
Trees – Grow useful trees and food forests
Insects – Raise beneficial insects and keep pests away
Animals – Raise healthy animals using the resources available
Kitchen – Prepare, ferment or preserve food grown on site
Appropriate technology – Use energy efficiently
Economics – Create a surplus
Project planning – Install a sustainable farming design
Ethics
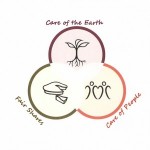
Ethics are moral principles that govern a person’s behavior. Three aspects sustainable farming ethics:
People care – Be considerate of everyone’s time, interests, thoughts and actions, including our own
Earth care – Care for the earth, the animals, the plants, trees, fungi, microbes, water, air
Fair share – Fairly distribute growth/surplus among humans and nature